Betsy would often tell her children, grandchildren, relatives, and friends of the fateful day when three members of a secret committee from the Continental Congress came to call upon her. Those representatives, George Washington, Robert Morris, and George Ross, asked her to sew the first flag. This meeting occurred in her home some time late in May 1776. George Washington was then the head of the Continental Army. Robert Morris, an owner of vast amounts of land, was perhaps the wealthiest citizen in the Colonies. Colonel George Ross was a respected Philadelphian and also the uncle of her late husband, John Ross.
Naturally, Betsy Ross already knew George Ross as she had married his nephew. Furthermore, Betsy was also acquainted with the great General Washington. Not only did they both worship at Christ Church in Philadelphia, but Betsy's pew was next to George and Martha Washington's pew. Her daughter recalled, "That she was previously well acquainted with Washington, and that he had often been in her house in friendly visits, as well as on business. That she had embroidered ruffles for his shirt bosoms and cuffs, and that it was partly owing to his friendship for her that she was chosen to make the flag." (For full text, see Affidavits.)
In June 1776, brave Betsy was a widow struggling to run her own upholstery business. Upholsterers in colonial America not only worked on furniture but did all manner of sewing work, which for some included making flags. According to Betsy, General Washington showed her a rough design of the flag that included a six-pointed star. Betsy, a standout with the scissors, demonstrated how to cut a five-pointed star in a single snip. Impressed, the committee entrusted Betsy with making our first flag.
Until that time, colonies and militias used many different flags. Some are famous, such as the "Rattlesnake Flag" used by the Continental Navy, with its venomous challenge, "Don't Tread on Me."
Another naval flag had a green pine tree on a white background. The one shown here is the "Liberty Tree" flag.
Naturally, Betsy Ross already knew George Ross as she had married his nephew. Furthermore, Betsy was also acquainted with the great General Washington. Not only did they both worship at Christ Church in Philadelphia, but Betsy's pew was next to George and Martha Washington's pew. Her daughter recalled, "That she was previously well acquainted with Washington, and that he had often been in her house in friendly visits, as well as on business. That she had embroidered ruffles for his shirt bosoms and cuffs, and that it was partly owing to his friendship for her that she was chosen to make the flag." (For full text, see Affidavits.)
In June 1776, brave Betsy was a widow struggling to run her own upholstery business. Upholsterers in colonial America not only worked on furniture but did all manner of sewing work, which for some included making flags. According to Betsy, General Washington showed her a rough design of the flag that included a six-pointed star. Betsy, a standout with the scissors, demonstrated how to cut a five-pointed star in a single snip. Impressed, the committee entrusted Betsy with making our first flag.
Until that time, colonies and militias used many different flags. Some are famous, such as the "Rattlesnake Flag" used by the Continental Navy, with its venomous challenge, "Don't Tread on Me."
Another naval flag had a green pine tree on a white background. The one shown here is the "Liberty Tree" flag.
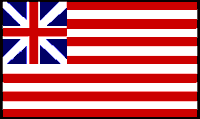
Other flags were quite similar to Britain's Union Jack or incorporated elements of it. A picture of the "Grand Union" flag is shown here.
This is not surprising. Many colonists considered themselves loyal subjects of Britain — many colonists came from Britain, and King George III ruled over the colonies.
On January 1, 1776, the Continental Army was reorganized in accordance with a Congressional resolution which placed American forces under George Washington's control. On that New Year's Day the Continental Army was laying siege to Boston which had been taken over by the British Army. Washington ordered the Grand Union flag hoisted above his base at Prospect Hill "in compliment of the United Colonies."
In Boston, on that New Year's Day, the Loyalists (supporters of Britain) had been circulating a recent King George speech, offering the Continental forces favorable terms if they laid down their arms. These Loyalists were convinced that the King's speech had impressed the Continentals into surrendering — as a sign of the Continentals' "surrender," the Loyalists mistook the flying of the Grand Union flag over Prospect Hill as a show of respect to King George. In fact, however, the Continentals knew nothing of the speech until later. Washington wrote in a letter dated January 4, "By this time, I presume, they begin to think it strange we have not made a formal surrender of our lines."
Obviously a new flag was needed.
According to Betsy Ross's dates and sequence of events, in May the Congressional Committee called upon her at her shop. She finished the flag either in late May or early June 1776. In July, the Declaration of Independence was read aloud for the first time at Independence Hall. Amid celebration, bells throughout the city tolled, heralding the birth of a new nation.
Much suffering and loss of life would result, however, before the United States would completely sever ties with Britain. Betsy Ross herself lost two husbands to the Revolutionary War. During the conflict the British appropriated her house to lodge soldiers. Through it all she managed to run her own upholstery business (which she continued operating for several decades after the war) and after the soldiers left, she wove cloth pouches which were used to hold gunpowder for the Continentals. (See The Story of Betsy Ross's Life for more information.)
On June 14, 1777, the Continental Congress, seeking to promote national pride and unity, adopted the national flag. "Resolved: that the flag of the United States be thirteen stripes, alternate red and white; that the union be thirteen stars, white in a blue field, representing a new constellation."
On January 1, 1776, the Continental Army was reorganized in accordance with a Congressional resolution which placed American forces under George Washington's control. On that New Year's Day the Continental Army was laying siege to Boston which had been taken over by the British Army. Washington ordered the Grand Union flag hoisted above his base at Prospect Hill "in compliment of the United Colonies."
In Boston, on that New Year's Day, the Loyalists (supporters of Britain) had been circulating a recent King George speech, offering the Continental forces favorable terms if they laid down their arms. These Loyalists were convinced that the King's speech had impressed the Continentals into surrendering — as a sign of the Continentals' "surrender," the Loyalists mistook the flying of the Grand Union flag over Prospect Hill as a show of respect to King George. In fact, however, the Continentals knew nothing of the speech until later. Washington wrote in a letter dated January 4, "By this time, I presume, they begin to think it strange we have not made a formal surrender of our lines."
Obviously a new flag was needed.
According to Betsy Ross's dates and sequence of events, in May the Congressional Committee called upon her at her shop. She finished the flag either in late May or early June 1776. In July, the Declaration of Independence was read aloud for the first time at Independence Hall. Amid celebration, bells throughout the city tolled, heralding the birth of a new nation.
Much suffering and loss of life would result, however, before the United States would completely sever ties with Britain. Betsy Ross herself lost two husbands to the Revolutionary War. During the conflict the British appropriated her house to lodge soldiers. Through it all she managed to run her own upholstery business (which she continued operating for several decades after the war) and after the soldiers left, she wove cloth pouches which were used to hold gunpowder for the Continentals. (See The Story of Betsy Ross's Life for more information.)
On June 14, 1777, the Continental Congress, seeking to promote national pride and unity, adopted the national flag. "Resolved: that the flag of the United States be thirteen stripes, alternate red and white; that the union be thirteen stars, white in a blue field, representing a new constellation."